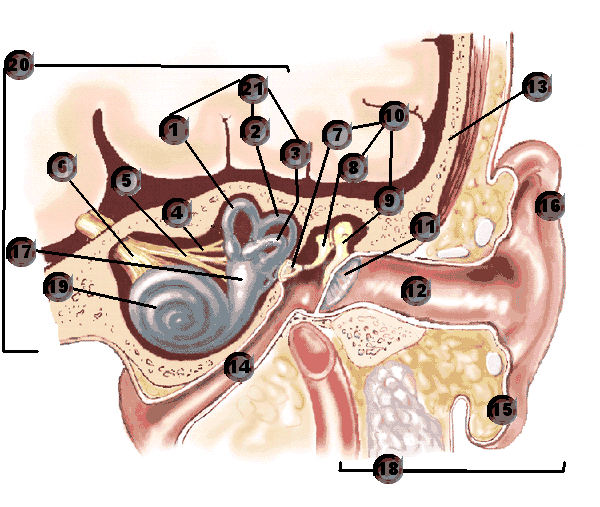

This condition causes an intense and brief but false sense that you're spinning or moving. An episode can be experience by a rapid change in head movement, such as when you turn over in bed, sit up or experience a blow to the head.
Vestibular neuritis viral infection of the vestibule nerve. Symptoms: intense, constant vertigo. If you also have sudden hearing loss, you may have labyrinthitis.
Inner ear: excessive buildup of fluid. syptoms: sudden episodes of vertigo. Possibly the experience of fluctuating hearing loss, ringing in the ear and the feeling of a plugged ear.
